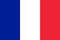
What is osteochondrosis
ICD-10 code
According to ICD-10, osteochondrosis has the code M42 and belongs to the category "Disorders of the musculoskeletal system and connective tissue" (group "dorsal cord disease", subgroup "dorsal cord disease").
Development causes and risk factors
- genetic predisposition. Congenital anomalies can lead to the development of diseases of the musculoskeletal system;
- hormonal imbalance. Endocrine disorders, being overweight or underweight can negatively impact the musculoskeletal system;
- age-related body changes. As a result, muscle, bone, and cartilage tissue are destroyed, and the discs wear out with age;
- spinal injuries and bruises. Many people spend long periods of time in one position, such as sitting at a desk, while others perform the same type of physical work. All of these can lead to damage to the bones and ligaments of the spine, as well as damage to the intervertebral discs;
- Degenerative changes in muscle tissue. These processes occur due to excessive tension on individual muscle groups, which often leads to osteochondrosis of the chest.
- sedentary lifestyle. Muscles atrophy, causing circulatory problems and improper bone formation.
Most people do not pay attention to their diet and eat food that is not healthy at all. As a result, nutritional deficiencies can occur that negatively affect the integrity, mobility, and elasticity of the intervertebral cartilage.
- low temperature;
- flatfoot;
- Complications following infectious diseases;
- overweight;
- Sedentary lifestyle;
- Spinal injury.
Types and symptoms
cervical osteochondrosis
- neck pain– With neck pain and limited movement; pain radiating into the shoulder area and the space between the shoulder blades; often tingling and burning sensations in the hands and fingers;
- Neck and cranial pain– Accompanied by pain from the neck to the top of the head, occipital part, shoulder girdle; muscle tension is characteristic, producing a feeling of petrification; headache, nausea, tinnitus, imbalance are observed;
- Neck and arm pain– Characterized by tingling, soreness, pulling and throbbing pain; turning and tilting the head can cause acute pain and body tension in the affected area, pain in the arms and fingers, leading to weakness in the upper limbs;
- discogenic root disease– Characterized by paroxysmal pain in the shoulders, forearms, and fingers, accompanied by numbness and coldness; symptoms worsen when coughing, sneezing, or turning the head sharply; may worsen at night, causing insomnia.
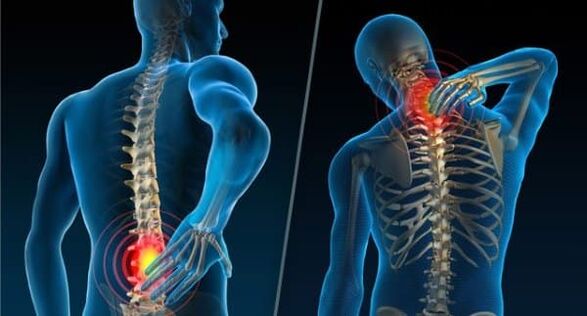
Thoracic osteochondrosis
- Chest pain or intercostal neuralgia– This is the stimulation or compression of the intercostal nerves by muscles and tissues. When bending, stooping and turning the body, it is accompanied by chest pain, under the ribs, in the front of the chest, and when inhaling and exhaling; the pain may radiate tobetween shoulder and shoulder blade;
- pain syndrome, in which the pain is intrinsic; pain can be felt in the chest and abdomen; the condition is aggravated by movement, coughing, sneezing, laughing; sensitivity disorders are observed.
Chest pain (chest pain) is one of the most severe symptoms a person can experience. Sometimes, even doctors cannot immediately determine the cause of chest pain and find out whether this symptom is a sign of a life-threatening condition for the patient.
Lumbosacral osteochondrosis
- Low back pain (acute low back pain)– Acute pain in the lumbar spine that occurs when lifting weights, doing physical activity or bending over; characterized by severe pain on the right or left side of the waist; they also differentiate low back pain from sciatica when the pain spreads to the buttocks and legs;
- Radiculovascular syndrome (nerve root ischemia)It occurs when the nerve radiculomedullary artery is damaged, accompanied by paralysis of the extensor and flexor muscles of the gluteal muscle group, and the foot is weak and droops without movement.
Spinal osteochondrosis with radiculovascular syndrome is a very dangerous pathology that presents with acute pain, since CSS is often the result of certain diseases.
development stage
- The initial stage begins with the loss of fluid reserves in the nucleus pulposus of the intervertebral disc. thereforeThe physiological position of the intervertebral disc and the structure of the nucleus pulposus are destroyed.
- Further progression of the disease (level one) is due to a decrease in disc height.Muscles and ligaments become overstrained and lose their ability to work properly.At this stage, vertebrae may shift.
- The second degree is characterized by changes in bone tissue.Joint formation, subluxation occurs.
- The third degree is determined by the following facts:Bone growths (osteophytes) form on the spine,This results in nerve root damage.
What is the difference between radiculitis and arthropathy?
Differential diagnostic methods are used to identify disease. This is a comprehensive approach that takes effort and time.
diagnosis

neurological examination
spinal myelography
Computed tomography (CT)
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR)
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
You cannot consent to treatment without an initial full diagnosis. This will only lead to worsening health conditions.
treatment method
medical treatement
- Painkillers and various analgesics;
- Medications to relieve spasms;
- vitamins B and C;
- Medications to relieve inflammation;
- Medications that promote blood circulation.
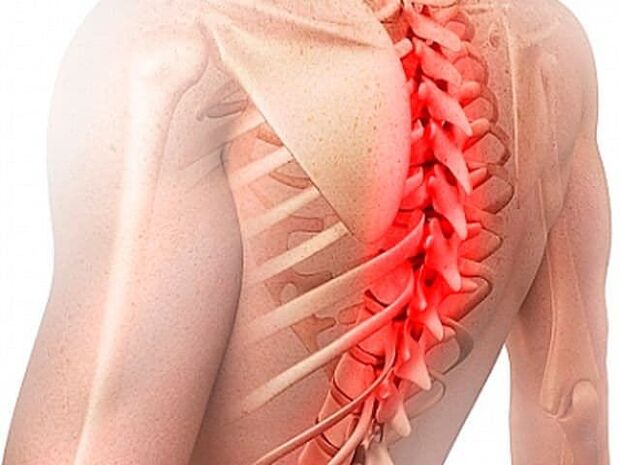
physiotherapy
- electrophoresis– Physiotherapy using electric fields modulated by electric current. This allows the drug to be introduced into the body. Helps relieve pain and muscle spasms;
- Magnet therapy. This painless physical therapy involves the positive effects of magnetic fields on the active cells of nerve and muscle fibers. Thereby activating the work of molecular structure and improving the functional characteristics of blood vessels;
- Ultrasound therapy. Ultrasound is sound waves produced in a range that cannot be detected by the human ear. As a result, blood circulation in the affected area improves, spasms are relieved, pain is eliminated, and inflammatory processes cease;
- vibration effect. The affected area is subjected to mechanical vibration;
- Balneotherapy. The essence of the method is the use of mineral water, which relaxes the muscles and has a beneficial effect on the musculoskeletal system. Use mineral water in the shower or bath.
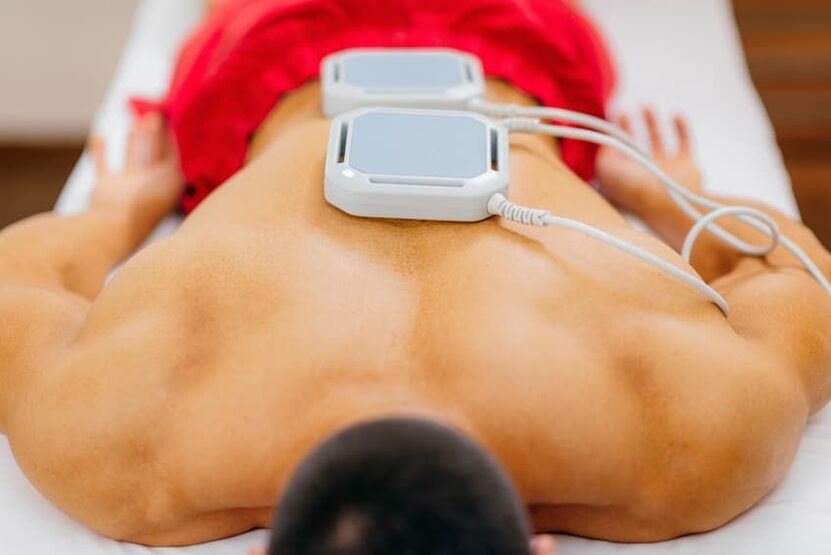
Physical therapy should be performed when symptoms subside and are pain-free. In the acute stage of the disease, the doctor chooses a set of procedures that will eliminate the painful syndrome. After appropriate physical therapy, the patient no longer experiences pain and the spine becomes more mobile, indicating recovery.
traditional method
- You need 300 grams of radish juice, 200 grams of honey and 100 grams of vodka. Mix all ingredients and lubricate affected area twice daily.
- You will need 1 tbsp. lake rye flour, 100 g butter, 1 tbsp. lake vinegar and 1 egg. Mix all ingredients and let sit for two days. Rub into affected area.
- Grate raw potatoes and mix with a little honey. Apply the prepared toothpaste to the sore area for 2 hours.
Traction
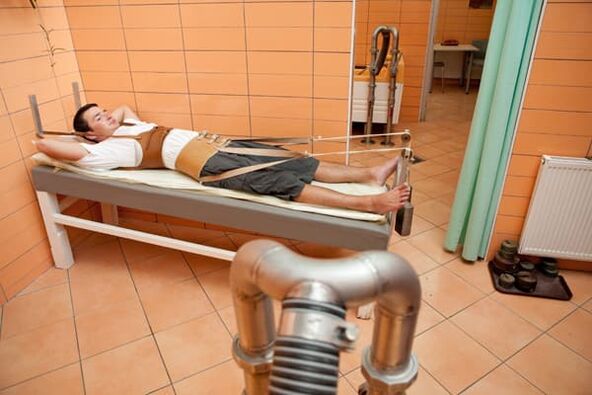
Under the influence of water, the distance between vertebrae increases, vasospasm in the affected area is eliminated, and blood supply improves.
Surgery
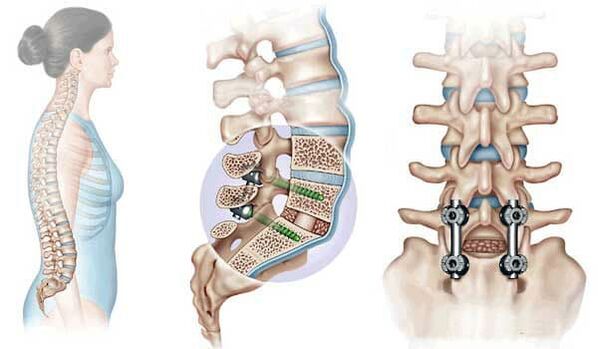
physiotherapy
complication
- Inflammatory diseases of the nerve roots (radiculitis, radiculopathy);
- intervertebral hernia;
- vegetative vascular dystonia;
- various neurological complications;
- severe headache, migraine;
- limb atrophy;
- spinal stenosis;
- Spondyloarthropathy (hyperplasia of the joint surface margins due to joint deformation);
- Spinal cord stroke.
If treatment is not started promptly, complications such as reproductive and urinary system organ dysfunction may occur.
prevention
- correctorganize a workplace;
- needed when you workshort breakdo light gymnastics;
- pay attention to your posture;
- DailyGait should be relaxed and unrestricted;
- Choose appropriate, comfortable pillows and a bouncy mattress.The sleeping surface should be flatbouncy;
- In your daily diet, you should try to eat less salty and sweet dishes and more calcium-rich foods. Vitamins C, E, and B are necessary to strengthen cartilage tissue and make it elastic.
- active lifestyle.
- preventivemassage.
- Medicinalgymnastics.
in conclusion
- Osteochondrosis is a degenerative disease of the human spine. Symptoms depend on the type of disease and where it occurs (neck, chest, lumbosacral area).
- Complications of the disease not only destroy the integrity of the spine but also significantly affect the function of other organ systems.
- Osteochondrosis can only be cured with comprehensive treatment, a combination of medication, physical therapy, and therapeutic exercises.
- Not complicatedPreventive measures will help protect your body from serious pathologies.